schemas
OpenAPI 3.0 and 3.1 diverge in schemas. OpenAPI 3.1 uses a newer draft of JSON Schema with less modifications.
Common properties
- type
- title
- description
- example (examples in OpenAPI 3.1)
- enum
- format
- properties
- items
- required
Nesting adds complexity to definitions. Polymorphism adds more complexity.
Excerpt from the OpenAPI 3.0 specification about schemas
The Schema Object allows the definition of input and output data types. These types can be objects, but also primitives and arrays. This object is an extended subset of the JSON Schema Specification Wright Draft 00.
For more information about the properties, see JSON Schema Core and JSON Schema Validation. Unless stated otherwise, the property definitions follow the JSON Schema.
Properties
The following properties are taken directly from the JSON Schema definition and follow the same specifications:
- title
- multipleOf
- maximum
- exclusiveMaximum
- minimum
- exclusiveMinimum
- maxLength
- minLength
- pattern (This string SHOULD be a valid regular expression, according to the Ecma-262 Edition 5.1 regular expression dialect)
- maxItems
- minItems
- uniqueItems
- maxProperties
- minProperties
- required
- enum
The following properties are taken from the JSON > Schema definition but their definitions were adjusted to the OpenAPI Specification.
- type - Value MUST be a string. Multiple types via an array are not supported.
- allOf - Inline or referenced schema MUST be of a Schema Object and not a standard JSON Schema.
- oneOf - Inline or referenced schema MUST be of a Schema Object and not a standard JSON Schema.
- anyOf - Inline or referenced schema MUST be of a Schema Object and not a standard JSON Schema.
- not - Inline or referenced schema MUST be of a Schema Object and not a standard JSON Schema.
- items - Value MUST be an object and not an array. Inline or referenced schema MUST be of a Schema Object and not a standard JSON Schema.
itemsMUST be present if thetypeisarray.- properties - Property definitions MUST be a Schema Object and not a standard JSON Schema (inline or referenced).
- additionalProperties - Value can be boolean or object. Inline or referenced schema MUST be of a Schema Object and not a standard JSON Schema. Consistent with JSON Schema,
additionalPropertiesdefaults totrue.- description - CommonMark syntax MAY be used for rich text representation.
- format - See Data Type Formats for further details. While relying on JSON Schema's defined formats, the OAS offers a few additional predefined formats.
- default - The default value represents what would be assumed by the consumer of the input as the value of the schema if one is not provided. Unlike JSON Schema, the value MUST conform to the defined type for the Schema Object defined at the same level. For example, if
typeisstring, thendefaultcan be"foo"but cannot be1.Alternatively, any time a Schema Object can be used, a Reference Object can be used in its place. This allows referencing definitions instead of defining them inline.
Additional properties defined by the JSON Schema specification that are not mentioned here are strictly unsupported.
Other than the JSON Schema subset fields, the following fields MAY be used for further schema documentation:
Fixed Fields
Field Name Type Description nullable booleanA truevalue adds"null"to the allowed type specified by thetypekeyword, only iftypeis explicitly defined within the same Schema Object. Other Schema Object constraints retain their defined behavior, and therefore may disallow the use ofnullas a value. Afalsevalue leaves the specified or defaulttypeunmodified. The default value isfalse.discriminator Discriminator Object Adds support for polymorphism. The discriminator is an object name that is used to differentiate between other schemas which may satisfy the payload description. See Composition and Inheritance for more details. readOnly booleanRelevant only for Schema "properties"definitions. Declares the property as "read only". This means that it MAY be sent as part of a response but SHOULD NOT be sent as part of the request. If the property is marked asreadOnlybeingtrueand is in therequiredlist, therequiredwill take effect on the response only. A property MUST NOT be marked as bothreadOnlyandwriteOnlybeingtrue. Default value isfalse.writeOnly booleanRelevant only for Schema "properties"definitions. Declares the property as "write only". Therefore, it MAY be sent as part of a request but SHOULD NOT be sent as part of the response. If the property is marked aswriteOnlybeingtrueand is in therequiredlist, therequiredwill take effect on the request only. A property MUST NOT be marked as bothreadOnlyandwriteOnlybeingtrue. Default value isfalse.xml XML Object This MAY be used only on properties schemas. It has no effect on root schemas. Adds additional metadata to describe the XML representation of this property. externalDocs External Documentation Object Additional external documentation for this schema. example Any A free-form property to include an example of an instance for this schema. To represent examples that cannot be naturally represented in JSON or YAML, a string value can be used to contain the example with escaping where necessary. deprecated booleanSpecifies that a schema is deprecated and SHOULD be transitioned out of usage. Default value is false.This object MAY be extended with Specification Extensions.
Data types and formats
The string, number, integer, boolean, and null types are atomic. The object and array types can be composed of atomic types and also composed of other objects and arrays. Nesting (or nested) describes when an object or array contains another object or array.
Visuals
enum
The enum property has a list of valid values. It should be valid against any declared types.
type: string
enum:
- house
- apartment
- recreation vehicle
- tent
- space station
Resources
- See
x-enumDescriptionsspecification extension for a way to describe theenumvalues. - See
maxDisplayedEnumValuesandsortEnumValuesAlphabeticallyfeatures.
Annotations
Various types support properties that are mostly for documentation purposes (not for request validation).
descriptiontitlereadOnlyandwriteOnlyexample(and in OAS 3.1examples)
description
The title and description keywords must be strings. A “title” will preferably be short, whereas a “description” will provide a more lengthy explanation about the purpose of the data described by the schema.
type: string
description: |
The description can use **Markdown**.
### This is a 3rd level heading
And this is a body paragraph with a [link to something interesting](#).The following shows how Redocly renders the schema description.

The description may also contain images and videos.
title
A “title” will preferably be short
type: string
title: Shalborn
description: |
The description can use **Markdown**.
### This is a 3rd level heading
And this is a body paragraph with a [link to something interesting](#).
The following shows how Redocly renders the title.

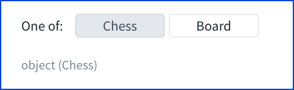
When the schema uses anyOf or oneOf the title is rendered in a button to select which schema is displayed.
anyOf:
- type: object
title: Chess
- type: object
title: BoardoneOf:
- type: object
title: Chess
- type: object
title: Board
readOnly and writeOnly
readOnlyindicates that a value should not be modified. It could be used to indicate that a PUT request that changes a value would result in a 400 Bad Request response.writeOnlyindicates that a value may be set, but will remain hidden.
The following example schema shows the use of readOnly and writeOnly properties. The same schema is used for the request and response.
paths:
/:
post:
summary: Sample API
description: Sample API description.
requestBody:
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: "#/components/schemas/ChessResult"
responses:
200:
description: Success
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: "#/components/schemas/ChessResult"
components:
schemas:
ChessResult:
type: object
properties:
id:
type: string
format: uuid
description: The system ID of the game.
readOnly: true
opponent:
type: string
description: The username of the opponent.
result:
type: string
description: The outcome of the game.
enum:
- won
- lost
- draw
gameCode:
type: string
format: password
description: Secret code to verify the game authenticity.
writeOnly: trueThe following shows that the properties and examples displayed respect the readOnly and writeOnly properties. The readOnly properties show in the response only. The writeOnly properties show in the request only.
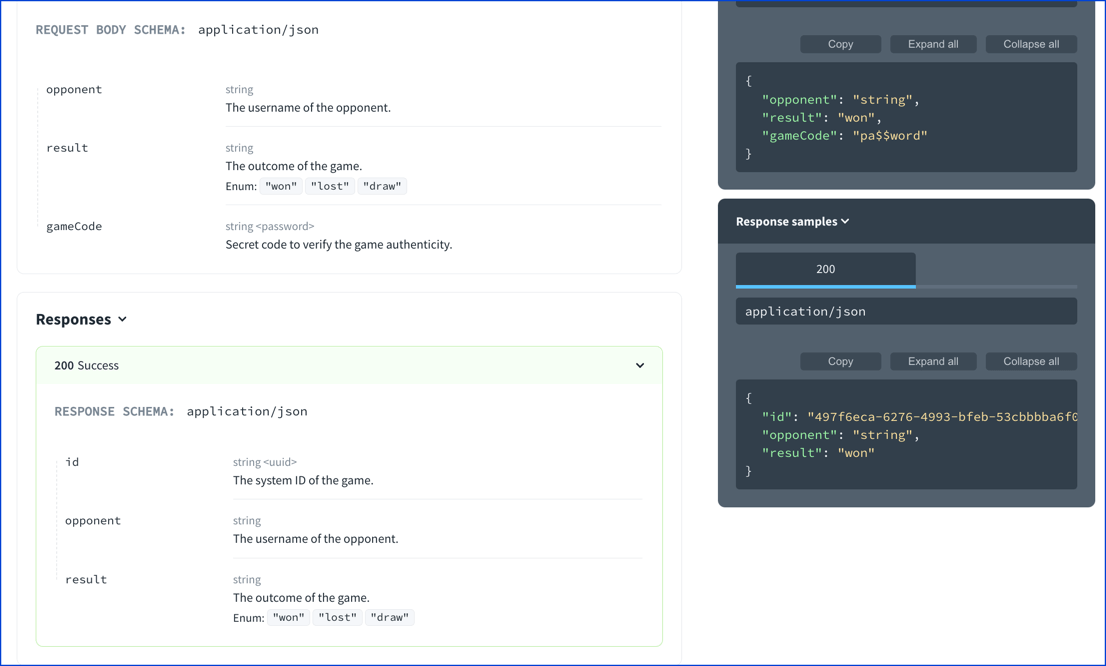
This behavior is reversed for webhooks. The readOnly properties show in the request only. The following example uses the same ChessResult schema as the previous example.
x-webhooks:
chessResultPosted:
post:
summary: Chess result posted
description: A webhook sent when a chess result is posted to webhook subscribers.
requestBody:
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: "#/components/schemas/ChessResult"
responses:
200:
description: Successwebhooks:
chessResultPosted:
post:
summary: Chess result posted
description: A webhook sent when a chess result is posted to webhook subscribers.
requestBody:
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: "#/components/schemas/ChessResult"
responses:
200:
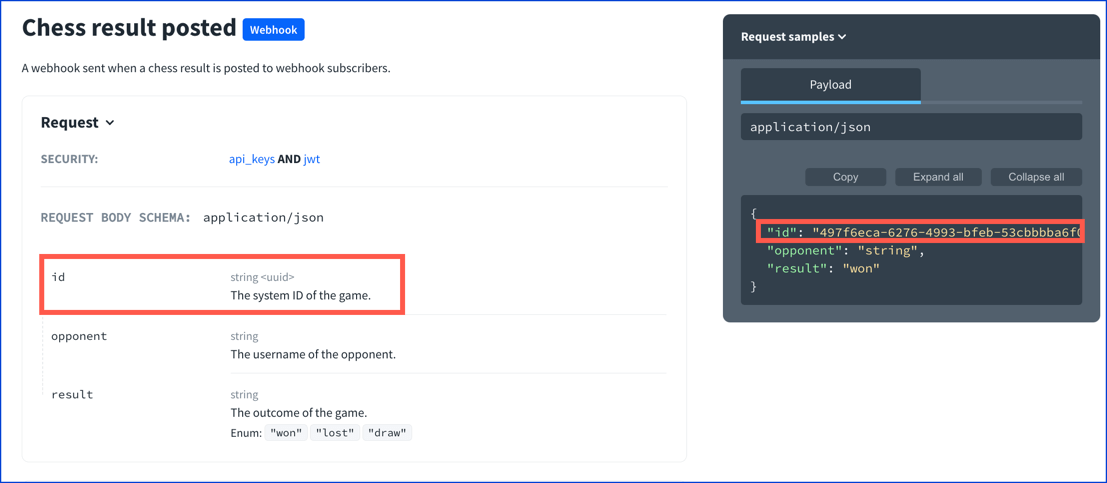
description: SuccessThe following image displays the readOnly properties displayed in the webhook request.
example and examples
In OAS 3.1, schema examples was introduced. Prior to that, a schema property has a single example. Note, schema examples are different from media-type examples.
The following definition shows schema examples defined on each property including the object.
ChessResult:
type: object
example:
opponent: GothamChess
properties:
opponent:
type: string
description: The username of the opponent.
example: Hikaru
result:
type: string
description: The outcome of the game.
example: lost
enum:
- won
- lost
- drawIn this case, Redocly gives priority to examples defined at the outer level. Therefore, the object example is displayed instead of each property example.
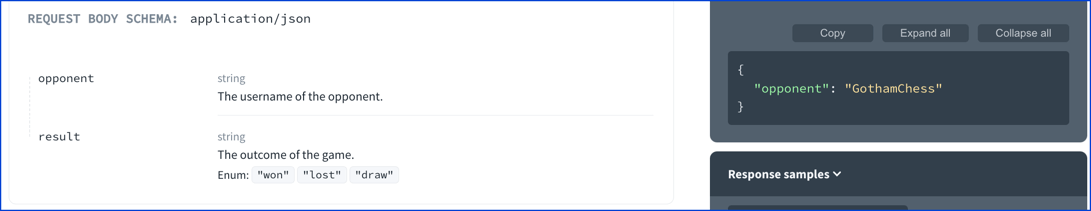
By removing the example from the object, each property will display its own example value.
ChessResult:
type: object
properties:
opponent:
type: string
description: The username of the opponent.
example: Hikaru
result:
type: string
description: The outcome of the game.
example: lost
enum:
- won
- lost
- draw
If there are multiple schema examples defined, Redocly will display the first example.
Priority is given, from top-to-bottom here in decreasing priority to:
- Media-type examples (Redocly will display multiple examples if defined)
- Schema examples on outer properties (Redocly will display the first example)
- Schema examples inner properties (Redocly will display the first example)
Types
- NamedSchemas
- SchemaMap
- Schema
- SchemaProperties
const Schema: NodeType = {
properties: {
externalDocs: 'ExternalDocs',
discriminator: 'Discriminator',
title: { type: 'string' },
multipleOf: { type: 'number', minimum: 0 },
maximum: { type: 'number' },
minimum: { type: 'number' },
exclusiveMaximum: { type: 'boolean' },
exclusiveMinimum: { type: 'boolean' },
maxLength: { type: 'number', minimum: 0 },
minLength: { type: 'number', minimum: 0 },
pattern: { type: 'string' },
maxItems: { type: 'number', minimum: 0 },
minItems: { type: 'number', minimum: 0 },
uniqueItems: { type: 'boolean' },
maxProperties: { type: 'number', minimum: 0 },
minProperties: { type: 'number', minimum: 0 },
required: { type: 'array', items: { type: 'string' } },
enum: { type: 'array' },
type: {
enum: ['object', 'array', 'string', 'number', 'integer', 'boolean', 'null'],
},
allOf: listOf('Schema'),
anyOf: listOf('Schema'),
oneOf: listOf('Schema'),
not: 'Schema',
properties: 'SchemaProperties',
items: (value: any) => {
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
return listOf('Schema');
} else {
return 'Schema';
}
},
additionalProperties: (value: any) => {
if (typeof value === 'boolean') {
return { type: 'boolean' };
} else {
return 'Schema';
}
},
description: { type: 'string' },
format: { type: 'string' },
default: null,
nullable: { type: 'boolean' },
readOnly: { type: 'boolean' },
writeOnly: { type: 'boolean' },
xml: 'Xml',
example: { isExample: true },
deprecated: { type: 'boolean' },
},
};